Personal Income Growth Disappoints In November 2013
Real Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) and Real Disposable Personal Income (DPI) are up. However, the rate of increase of income continues to fall further behind the rate of increase of spending.
- The market looks at current values (not real inflation adjusted) and was expecting a PCE (expenditures) rise of 0.5% to 0.7% (versus 0.5% actual), and a rise in DPI (income) of 0.5% (versus 0.1% actual). In other words, expenditures were at expectations whilst income was well under expectations.
- The monthly fluctuations are confusing. Looking at the 3 month trend rate of growth, income trend is down, whilst expenditures are trending up.
- Real Personal Income is up 0.6% year-over-year, and real personal expenditures are up 2.6% year-over-year. The gap between income and expenditures opened up again this month.
- this data is very noisy and as usual includes backward revision (detailed below) making real time analysis problematic – and the backward revisions this month are moderate.
- Earlier this week, the third estimate of 3Q2013 GDP indicated the economy was growing at 4.1%.
- The savings rate continues to be low, and again declined marginally this month.
The inflation adjusted income and consumption are “chained”, and headline GDP is inflation adjusted. This means the impact to GDP is best understood by looking at the chained numbers. Econintersect believes year-over-year trends are very revealing in understanding economic dynamics.
Per capita inflation adjusted expenditure has exceeded the pre-recession peak.
Seasonally and Inflation Adjusted Expenditure Per Capita

Per capita inflation adjusted income is above pre-recession levels.
Seasonally and Inflation Adjusted Income Per Capita

Backward revisions this month:
Estimates for personal income and DPI have been revised for July through October. Changes in personal income, in current-dollar and chained (2009) dollar DPI, and in current-dollar and chained (2009) dollar PCE for September and October — revised and as published in last month’s release — are shown below.
The graph below illustrates the relationship between income (DPI) and expenditures (PCE) – showing clearly income and expenditures grow at nearly the same rate over time. This is the second month that income (which had caught up with expenditures), fell further behind again.
Indexed to Jan 2000, Growth of Real Disposable Income (blue line) to Real Expenditures (red line)
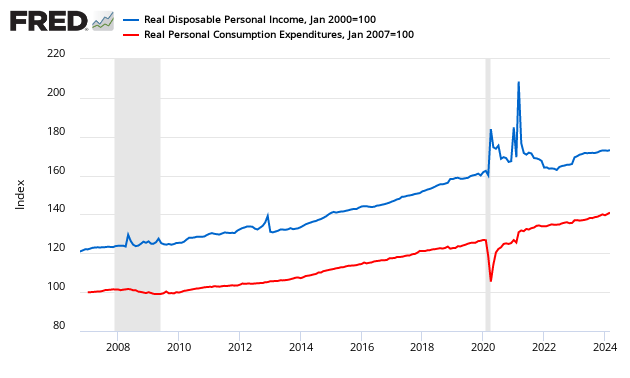
The long term trend is that the consumer is spending more of its income – but the 2013 trend is that the consumer is spending less of its income.
Seasonally Adjusted Spending’s Ratio to Income (a declining ratio means consumer is spending less of its Income)

PCE is the spending of consumers. In the USA, the consumer is the economy. Likewise, personal income is the money consumers earn to spend. Even though most analysts concentrate on personal expenditures because GDP is based on spending, increases in personal income allow consumers the option to spend more.
There is a general correlation of PCE to GDP (PCE is a component of GDP). PCE is a fairly noisy index and subject at times to significant backward revision (see caveats below).
Seasonally and Inflation Adjusted Year-over-Year Change of Personal Consumption Expenditures (blue line) to GDP (red line)

Econintersect and GDP uses the inflation adjusted (chained) numbers. Disposable Personal Income (DPI) is the income after the taxes.
Seasonally & Inflation Adjusted Percent Change From the Previous Month – Personal Disposable Income (red line) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (blue line)

Yet year-over-year growth is not exceptional with both consumption and income below GDP growth – and income growth still lagging consumption.
Seasonally & Inflation Adjusted Year-over-Year Change – Personal Disposable Income (red line) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (blue line)

The savings rate has been bouncing around – but the general trend is down. In an economy driven by consumers, a higher savings rate does not bode well for increased GDP. This is one reason GDP may not be a good single metric of economic activity. The question remains what is the optimal savings rate for the current demographics. It might be expected that as people near retirement, the savings rate rises and after people retire, savings rate falls. Econintersect is not aware of any study which documents this effect. The graph below is from BEA table 2.6. – and shows a significant fall in savings rate for January 2013 – and now a recovery is continuing. The savings rate is now 4.2% – now down three months in a row
Personal Savings as a Percentage of Disposable Personal Income

And one look at the different price changes seen by the BEA in this PCE release versus the BEA’s GDP and BLS’s Consumer Price Index (CPI). We should note that the inflation adjustment is for PCE and Personal Income is lower than the ones used for GDP and CPI.
Year-over-Year Change – PCE’s Price Index (blue line) versus CPI-U (red line) versus GDP Deflator (green line)

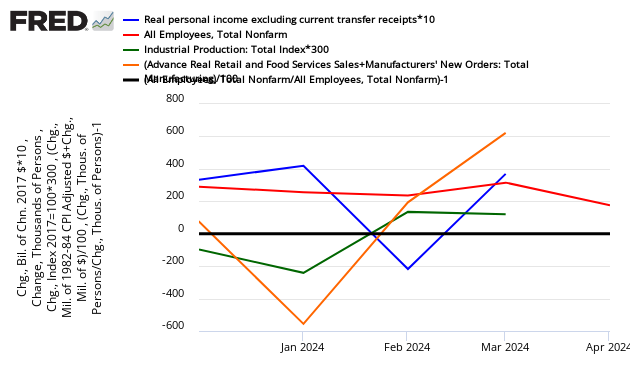
Finally for recession watchers, here is the graph below, here are the elements used to mark a recession. (1) personal income less transfer payments, in real terms and (2) employment. In addition, we refer to two indicators with coverage primarily of manufacturing and goods: (3) industrial production and (4) the volume of sales of the manufacturing and wholesale-retail sectors adjusted for price changes.
If a line falls below the 0 (black line) – that sector is contracting from the previous month. Personal income is the blue line. Note – the below graph uses multipliers to make movements more obvious (ignore the value of the scale, only consider whether the graph is above [good] or below [bad] the zero line).
Month-over-Month Growth Personal Income less transfer payments (blue line), Employment (red line), Industrial Production (green line), Business Sales (orange line)
Caveats on the Use of Personal Income and Consumption Expenditure Data
PCE is a fairly noisy index and subject at times to significant backward revision. This index cannot be relied upon in real time.
This personal income and personal consumption expenditure data by itself is not a good tool to warn of an upcoming recession. Econintersect has shown that PCE is a distraction for recession watchers, with moves over a few months having a 30% accuracy of indicating a recession start, and a 70% incidence of indicating a non-recessionary event. The graph below shows the lack of correlation. Note, however, that PCE does have prolonged declines over many months associated with recessions but these long declines are not very good in “predicting” a recession until it is already underway.

Readers are warned that this article is based on seasonally adjusted data. Monthly non-adjusted data is available with a delay of several months.
None.